Schema Search
In-memory natural language schema search over database schemas
Schema Search
Note: The project has moved to a new repo and is being maintained by SignalPilot Labs. The code in the current repo is only available for reference.
An MCP Server for Natural Language Search over RDBMS Schemas. Find exact tables you need, with all their relationships mapped out, in milliseconds. No vector database setup is required.
Why
You have 200 tables in your database. Someone asks "where are user refunds stored?"
You could:
- Grep through SQL files for 20 minutes
- Pass the full schema to an LLM and watch it struggle with 200 tables
Or build schematic embeddings of your tables, store in-memory, and query in natural language in an MCP server.
Benefits
- No vector database setup is required
- Small memory footprint -- easily scales up to 1000 tables and 10,000+ columns.
- Millisecond query latency
Install
Fast by default - Base install uses only BM25/fuzzy search (no PyTorch):
# Minimal install (BM25 + fuzzy only, ~10MB)
pip install "schema-search[postgres]"
# With semantic/hybrid search support (~500MB with PyTorch)
pip install "schema-search[postgres,semantic]"
# With LLM chunking
pip install "schema-search[postgres,semantic,llm]"
# With MCP server
pip install "schema-search[postgres,semantic,mcp]"
# Other databases
pip install "schema-search[mysql,semantic]" # MySQL
pip install "schema-search[snowflake,semantic]" # Snowflake
pip install "schema-search[bigquery,semantic]" # BigQuery
pip install "schema-search[databricks,semantic]" # Databricks
Extras:
[semantic]: Enables semantic/hybrid search and CrossEncoder reranking (adds sentence-transformers)[llm]: Enables LLM-based schema chunking (adds openai)[mcp]: MCP server support (adds fastmcp)
Configuration
Edit config.yml:
logging:
level: "WARNING"
embedding:
location: "memory" # Options: "memory", "vectordb" (coming soon)
model: "multi-qa-MiniLM-L6-cos-v1"
metric: "cosine" # Options: "cosine", "euclidean", "manhattan", "dot"
batch_size: 32
show_progress: false
cache_dir: "/tmp/.schema_search_cache"
chunking:
strategy: "raw" # Options: "raw", "llm"
max_tokens: 256
overlap_tokens: 50
model: "gpt-4o-mini"
search:
# Search strategy: "semantic" (embeddings), "bm25" (BM25 lexical), "fuzzy" (fuzzy string matching), "hybrid" (semantic + bm25)
strategy: "bm25"
initial_top_k: 20
rerank_top_k: 5
semantic_weight: 0.67 # For hybrid search (bm25_weight = 1 - semantic_weight)
hops: 1 # Number of foreign key hops for graph expansion (0-2 recommended)
reranker:
# CrossEncoder model for reranking. Set to null to disable reranking
model: null # "Alibaba-NLP/gte-reranker-modernbert-base"
schema:
include_columns: true
include_indices: true
include_foreign_keys: true
include_constraints: true
output:
format: "markdown" # Options: "json", "markdown"
limit: 5 # Default number of results to return
MCP Server
Integrate with Claude Desktop or any MCP client.
Setup
Add to your MCP config (e.g., ~/.cursor/mcp.json or Claude Desktop config):
Using uv (Recommended):
{
"mcpServers": {
"schema-search": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": [
"schema-search[postgres,mcp]",
"postgresql://user:pass@localhost/db",
"optional/path/to/config.yml",
"optional llm_api_key",
"optional llm_base_url"
]
}
}
}
Using pip:
{
"mcpServers": {
"schema-search": {
// conda: /Users/<username>/opt/miniconda3/envs/<your env>/bin/schema-search",
"command": "path/to/schema-search",
"args": [
"postgresql://user:pass@localhost/db",
"optional/path/to/config.yml",
"optional llm_api_key",
"optional llm_base_url"
]
}
}
}
The LLM API key and base url are only required if you use LLM-generated schema summaries (config.chunking.strategy = 'llm').
CLI Usage
schema-search "postgresql://user:pass@localhost/db" "optional/path/to/config.yml"
Optional args: [config_path] [llm_api_key] [llm_base_url]
The server exposes schema_search(query, hops, limit) for natural language schema queries.
Python Use
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from schema_search import SchemaSearch
# PostgreSQL
engine = create_engine("postgresql://user:pass@localhost/db")
sc = SchemaSearch(
engine=engine,
config_path="optional/path/to/config.yml", # default: config.yml
llm_api_key="optional llm api key",
llm_base_url="optional llm base url"
)
sc.index(force=False) # default is False
results = sc.search("where are user refunds stored?")
# Default output is markdown - render with str()
print(results) # Formatted markdown with schemas, relationships, and scores
# Access underlying data as dictionary
result_dict = results.to_dict()
for result in result_dict['results']:
print(result['table']) # "refund_transactions"
print(result['schema']) # Full column info, types, constraints
print(result['related_tables']) # ["users", "payments", "transactions"]
# Override output format explicitly
json_results = sc.search("where are user refunds stored?", output_format="json")
print(json_results) # JSON formatted string
# Override hops, limit, search strategy, and output format
results = sc.search("user_table", hops=1, limit=5, search_type="hybrid", output_format="markdown")
sc.index() automatically detects schema changes and refreshes cached metadata, so you rarely need to force a reindex manually.
Database Connection Strings
Schema Search uses SQLAlchemy connection strings:
# PostgreSQL
engine = create_engine("postgresql://postgres:mypass@localhost:5432/mydb")
# MySQL
engine = create_engine("mysql+pymysql://root:mypass@localhost:3306/mydb")
# Snowflake
engine = create_engine("snowflake://myuser:mypass@xy12345.us-east-1/MYDB/PUBLIC?warehouse=COMPUTE_WH&role=ANALYST")
# BigQuery
engine = create_engine("bigquery://my-project/my-dataset")
# Databricks
token = "dapi..."
host = "dbc-xyz.cloud.databricks.com"
http_path = "/sql/1.0/warehouses/abc123"
catalog = "main"
schema = "default" # Optional
# Without schema (queries across all schemas in catalog)
engine = create_engine(
f"databricks://token:{token}@{host}?http_path={http_path}&catalog={catalog}",
connect_args={"user_agent_entry": "schema-search"}
)
# With schema (limits to specific schema)
engine = create_engine(
f"databricks://token:{token}@{host}?http_path={http_path}&catalog={catalog}&schema={schema}",
connect_args={"user_agent_entry": "schema-search"}
)
Search Strategies
Schema Search supports four search strategies:
- bm25: Lexical search using BM25 ranking algorithm (no ML dependencies)
- fuzzy: String matching on table/column names using fuzzy matching (no ML dependencies)
- semantic: Embedding-based similarity search using sentence transformers (requires
[semantic]) - hybrid: Combines semantic and bm25 scores (default: 67% semantic, 33% bm25) (requires
[semantic])
Each strategy performs its own initial ranking, then optionally applies CrossEncoder reranking if reranker.model is configured (requires [semantic]). Set reranker.model to null to disable reranking.
Performance Comparison
We benchmarked on the Spider dataset (1,234 train queries across 18 databases) using the default config.yml.
Memory: The embedding model requires ~90 MB and the optional reranker adds ~155 MB. Actual process memory depends on your Python runtime.
Without Reranker (reranker.model: null)
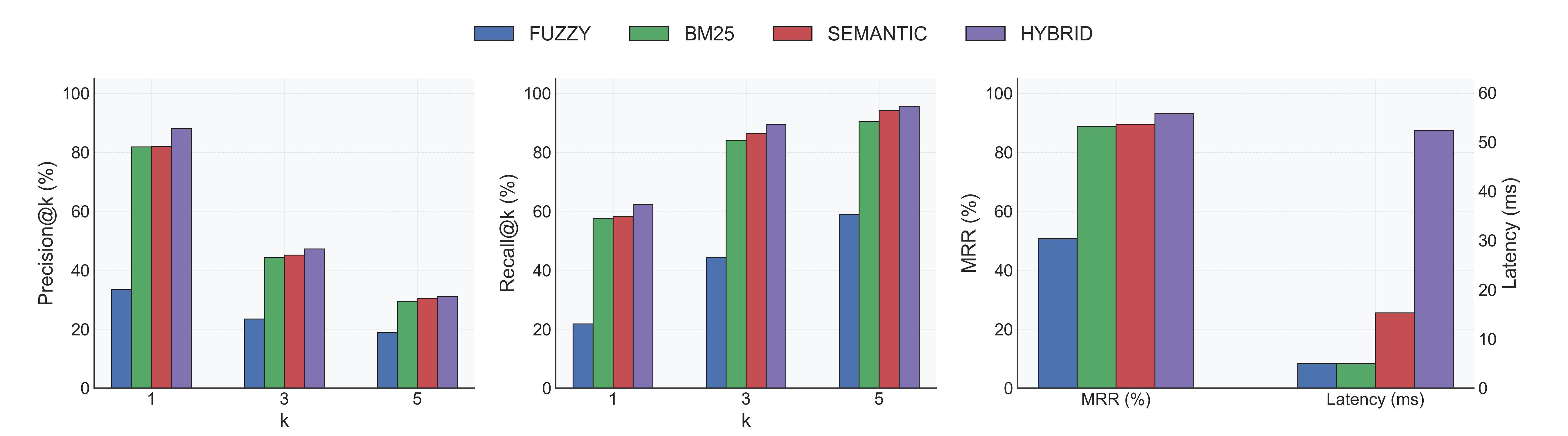
- Indexing: 0.22s ± 0.08s per database (18 total).
- Accuracy: Hybrid leads with Recall@1 62% / MRR 0.93; Semantic follows at Recall@1 58% / MRR 0.89.
- Latency: BM25 and Fuzzy return in ~5ms; Semantic spends ~15ms; Hybrid (semantic + fuzzy) averages 52ms.
- Fuzzy baseline: Recall@1 22%, highlighting the need for semantic signals on natural-language queries.
With Reranker (Alibaba-NLP/gte-reranker-modernbert-base)
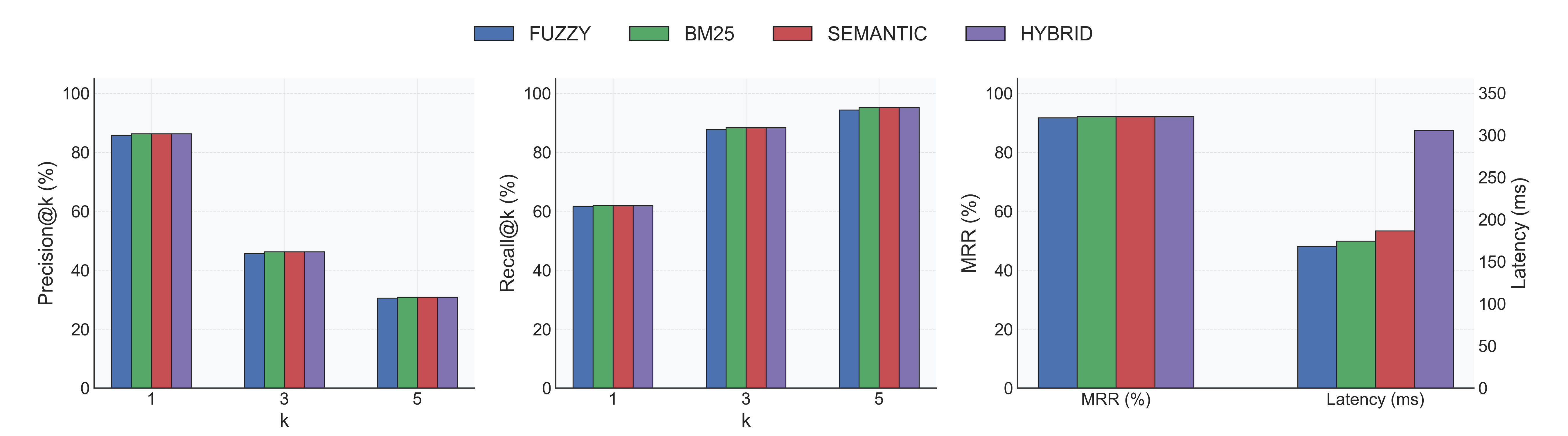
- Indexing: 0.25s ± 0.05s per database (same 18 DBs).
- Accuracy: All strategies converge around Recall@1 62% and MRR ≈ 0.92; Fuzzy jumps from 51% → 92% MRR.
- Latency trade-off: Extra CrossEncoder pass lifts per-query latency to ~0.18–0.29s depending on strategy.
- Recommendation: Enable the reranker when accuracy matters most; disable it for ultra-low-latency lookups.
You can override the search strategy, hops, and limit at query time:
# Use fuzzy search instead of default
results = sc.search("user_table", search_type="fuzzy")
# Use BM25 for keyword-based search
results = sc.search("transactions payments", search_type="bm25")
# Use hybrid for best of both worlds
results = sc.search("where are user refunds?", search_type="hybrid")
# Override hops and limit
results = sc.search("user refunds", hops=2, limit=10) # Expand 2 hops, return 10 tables
# Disable graph expansion
results = sc.search("user_table", hops=0) # Only direct matches, no foreign key traversal
Output Formats
Schema Search returns a SearchResult object that can be rendered in multiple formats:
- markdown (default): Formatted markdown with hierarchical table schemas
- json: Structured JSON output
The SearchResult object has:
__str__()method: Renders using the configured format (markdown or json).to_dict()method: Returns raw dictionary for programmatic access
Configure the default format in config.yml:
output:
format: "markdown" # or "json"
limit: 5 # Default number of results
Override at query time:
# Default markdown output - just print the object
results = sc.search("user payments")
print(results) # Formatted markdown
# Access underlying data as dictionary
data = results.to_dict()
print(data['results'][0]['table']) # "users"
# Override to JSON format
json_results = sc.search("user payments", output_format="json")
print(json_results) # JSON formatted string
Markdown output includes:
- Table name and relevance score
- Primary keys and columns with types/constraints
- Foreign key relationships
- Indices and constraints
- Related tables from graph expansion
- Matched content chunks
LLM Chunking
Use LLM to generate semantic summaries instead of raw schema text (requires [llm] extra):
- Install:
pip install "schema-search[postgres,llm]" - Set
strategy: "llm"inconfig.yml - Pass API credentials:
sc = SchemaSearch(
engine,
llm_api_key="sk-...",
llm_base_url="https://api.openai.com/v1/" # optional
)
How It Works
- Extract schemas from database using SQLAlchemy inspector
- Chunk schemas into digestible pieces (markdown or LLM-generated summaries)
- Initial search using selected strategy (semantic/BM25/fuzzy)
- Expand via foreign keys to find related tables (configurable hops)
- Optional reranking with CrossEncoder to refine results
- Return top tables with full schema and relationships
Cache stored in /tmp/.schema_search_cache/ (configurable in config.yml)
License
MIT
Related Servers
AWS Athena
Run SQL queries on data in Amazon S3 using AWS Athena.
Memory Cache Server
An MCP server that reduces token consumption by efficiently caching data between language model interactions.
FDA Data MCP
FDA-only compliance data MCP (recalls, warning letters, inspections, 483s, approvals, CFR parts).
GLEIF MCP Server
Access the Global Legal Entity Identifier (LEI) database for company verification, KYC, and corporate ownership research via GLEIF's public API.
MCP MySQL Server
An MCP server based on Spring AI that executes arbitrary SQL queries against a configured MySQL database.
Cryptocurrency Daemon
An MCP server for interacting with cryptocurrency daemon RPC interfaces.
FinanceMCP
Provides real-time financial data using the Tushare API.
MongoDB Atlas
A server for managing data in MongoDB Atlas, providing secure and scalable data management through RESTful APIs.
CData SAP Hybris C4C
A read-only MCP server for querying live SAP Hybris C4C data, powered by the CData JDBC Driver.
Rails PG Extras MCP
An MCP interface for the rails-pg-extras gem, providing PostgreSQL metadata and performance analysis through LLM prompts.